Is Rent Still a Cost Burden to People Living in the U.S.?
September 13, 2023

The cost of living in the United States has been growing at a rate that many people struggle to keep up with, especially regarding rent. What is causing rent to increase so sharply? Since 2020, there have been many factors that have been driving up the cost of rent. One of the most significant factors is inflation. Higher costs for labor and supply cause landlords to pass these costs down to renters. Not only is there a need for more inventory in the housing market, but there is a shortage of affordable rental properties across the country. This lack of inventory is causing rent prices to be more competitive for renters, despite seeing an increase in wages. The shortage is also caused by prospective home buyers who remain renters due to the current housing market barriers. How deep are rental costs cutting into Americans’ budgets and what are the impacts in Virginia?
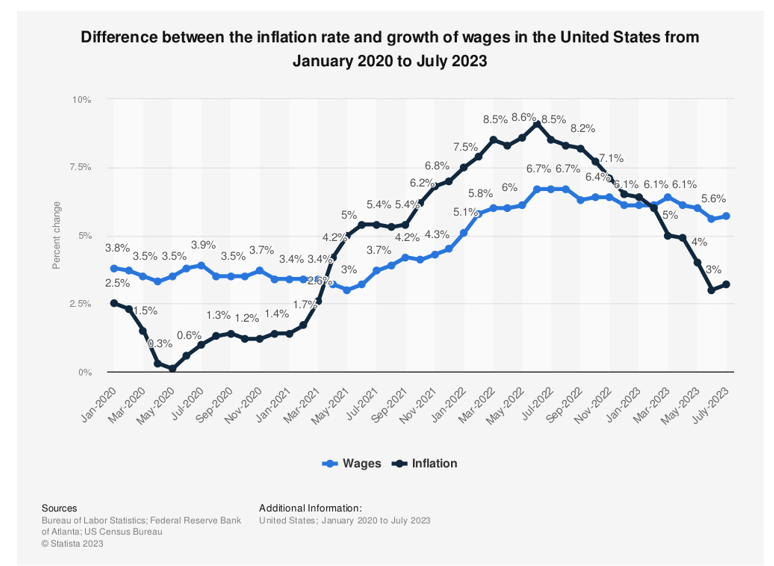
Wages and Inflation
According to recent Census Bureau data, median household income (all household types) across the U.S. was estimated at $74,580 in 2022, lower than the $76,330 estimated for 2021. In Virginia, the median household income is $80,615, according to recent 2021 census data, a slight drop from $82,214 in 2020. In 2022, American wages were growing steadily but at a slower rate than inflation. This rise in the cost of living made many people concerned about the overall economy, as their budgets took a major hit last year despite making more money. Higher wage earners are also being sidelined because of low inventory and intense competition in the market. Most of these high-income earners can be somewhat aggressive in their search for a rental home, which can drive up rental costs. The Fed’s efforts in raising interest rates have slowed inflation so far in 2023. Year-over-year inflation has been moderate in recent months, and many experts expect it to continue to slow down towards the end of the year. According to the latest Consumer Price Index, shelter costs contributed 90% of the total inflation in July.
Rent Costs
Throughout the nation, the rent-to-income ratio (RTI) rose above 30% last year for the first time in 25 years. In the first quarter of 2023, a seasonal drop in the multifamily market saw RTI decline by 0.9% to 29.6%, according to Moody Analytics. Though rents may seem to be softening throughout some parts of the U.S., it is still unpleasantly high.

In Virginia, rent grew by 2.8% in the second quarter of 2023, which is noticeably slower compared to last year’s Q2 growth of 9.2%, per our recent multifamily report. The Richmond metro area accounted for the smallest growth in rent, with an increase of 1.3% in the second quarter compared to last year, and the Harrisonburg metro area had the most robust rental growth of 7.9% in the second quarter. According to Zillow, rent cost in Virginia is 5% lower than the national average, and the median rent in the commonwealth so far this year is $1,989. By federal standards, a household is considered to be “housing cost burdened” if they spend more than 30% of their gross income on housing expenses and paying 50% or more means the household is “severely cost-burdened.”
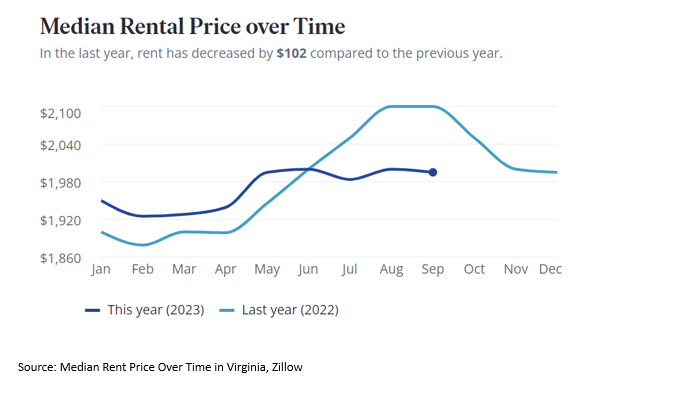
Housing costs continue to be the biggest expense for most Americans. This expense can be a burden to those who make low wages and have a lack of affordable rental homes to choose from. The multifamily market has encountered pressure from high demand, but low supply is still a major issue in the market.
You might also like…
Midway Through 2024, Virginia Home Sales Activity Slightly Outpacing Last Year
By Robin Spensieri - July 24, 2024
According to the June 2024 Virginia Home Sales Report released by Virginia REALTORS®, there were 10,018 homes sold across the commonwealth last month. This is 974 fewer sales… Read More
Three Multifamily Market Trends from the Second Quarter of 2024
By Sejal Naik - July 16, 2024
Each quarter, through its Multifamily Market report, the research team at Virginia REALTORS® analyzes the trends and changes in the multifamily market. Here, we share the key highlights… Read More
Takeaways From the JCHS 2024 State of the Nation’s Housing
By Dominique Fair - July 15, 2024
The Joint Center for Housing Studies from Harvard University released this year’s State of the Nation’s Housing report highlighting the impact today’s market is having on both homeowners… Read More