Inflation Trends in 2023: What Do They Mean for the Housing Market?
March 3, 2023

Inflation levels in the United States reached a more than 40-year high of 9.1% during the summer of 2022. While the latest report from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that inflation has simmered down to 6.4% at the start of 2023, consumer prices have increased significantly from just a few years ago.
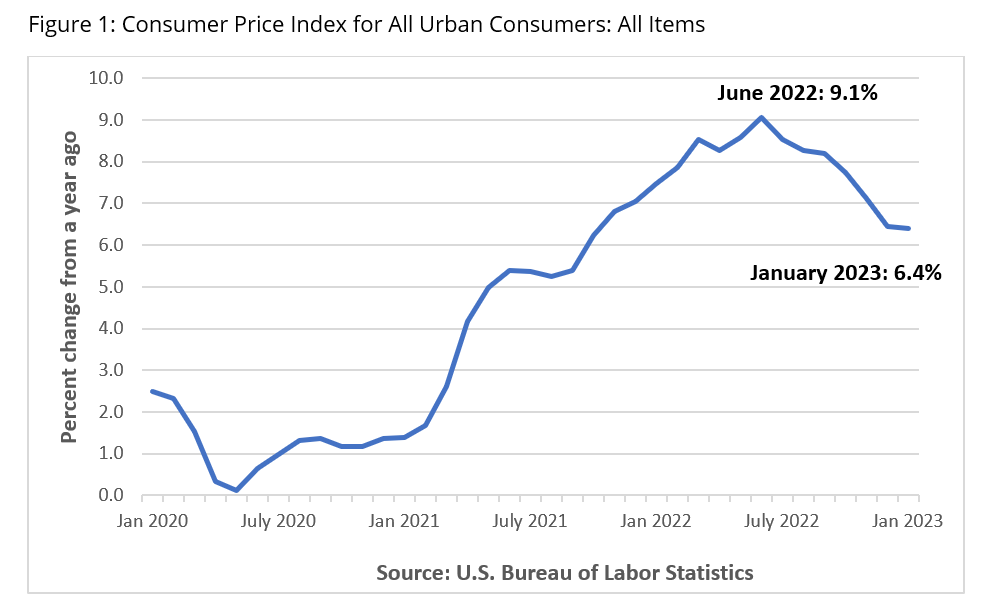
The increase in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in January can be attributed to a combination of increases and decreases in its various component indexes. Housing costs, which account for about 40% of the index, went up by 0.7% since December 2022 and increased by 7.9% from a year ago. The trend in rising rental costs is substantiated by an increase of 8.6% in the rent index over the past year. As compared to 12 months ago, food prices have also soared by 10.1%. Transportation costs, one of the top component indexes of the CPI, have seen a decline since their peak levels in summer 2022, albeit still having increased from a year ago. This could be due to the recent downward trend in the index for used cars and trucks, which fell by 1.9% since December 2022 and by 11.6% from over a year ago. Prices of other smaller components of CPI, such as apparel, medical care, recreation, and education and communication, increased moderately as well.
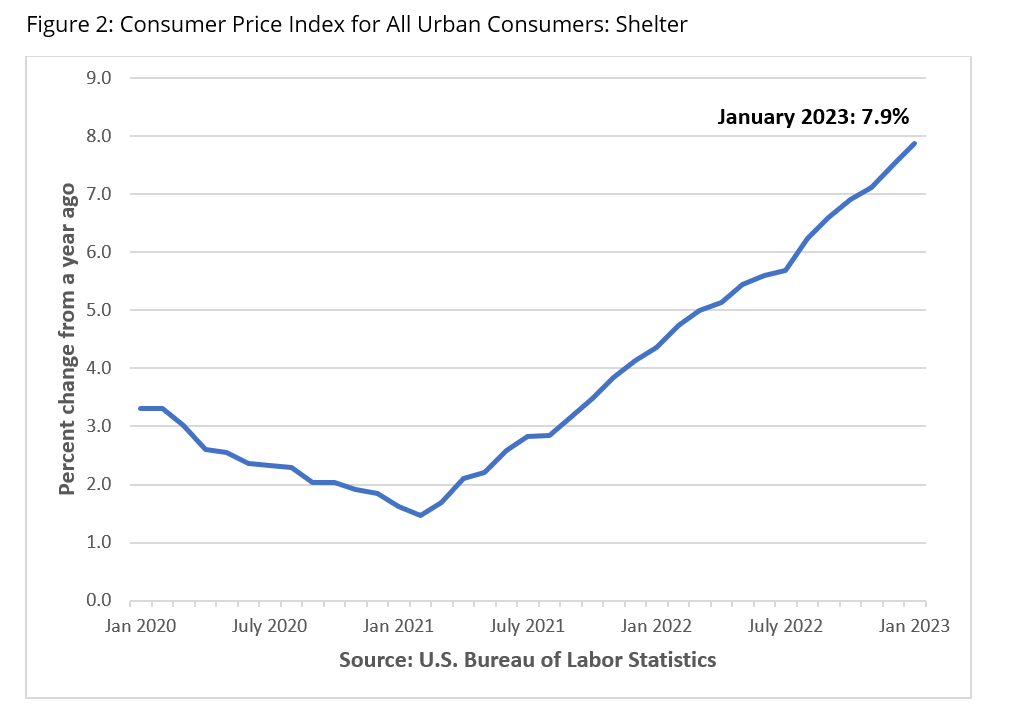
Since housing costs remain the largest contributor to the increase in inflation, let’s look at the ways in which inflation could affect the housing market in the coming months.
Rise in Construction Costs
High inflation affects the cost of materials required to construct houses. This will make building new homes or renovating existing homes an expensive endeavor. Such an increase in costs could trickle down and increase the prices of newly constructed homes or delay new construction projects.
Slowdown in Home Sales Activity
The increased home purchases of late-2020 and 2021 were fueled by pent up savings. As everyday costs rise, the expenses are chipping away at household savings. This will make potential home buyers weary of putting their money towards a home purchase and could cause a slowdown in home sales.
Increased Rental Market Activity & Rising Rental Prices
To respond to rising inflation, the Federal Reserve increases its federal funds rate, as it has been doing since the beginning of 2022. Banks and mortgage lenders use the federal funds rate as a base when determining lending rates. A subsequent increase in mortgage rates could keep buyers from receiving favorable mortgage terms. Consequently, many potential home buyers might continue to rent, leading to increased demand for rental units and further fuel the rise in rental prices.
As the narrative for the housing market of 2023 pans out, given the continued discourse about rising costs, inflation will be an important economic indicator to track in the near future.
For more information on demographic and economic trends in Virginia, be sure to check out Virginia REALTORS® other Economic Insights blogs and our Data page.
You might also like…
Midway Through 2024, Virginia Home Sales Activity Slightly Outpacing Last Year
By Robin Spensieri - July 24, 2024
According to the June 2024 Virginia Home Sales Report released by Virginia REALTORS®, there were 10,018 homes sold across the commonwealth last month. This is 974 fewer sales… Read More
Three Multifamily Market Trends from the Second Quarter of 2024
By Sejal Naik - July 16, 2024
Each quarter, through its Multifamily Market report, the research team at Virginia REALTORS® analyzes the trends and changes in the multifamily market. Here, we share the key highlights… Read More
Takeaways From the JCHS 2024 State of the Nation’s Housing
By Dominique Fair - July 15, 2024
The Joint Center for Housing Studies from Harvard University released this year’s State of the Nation’s Housing report highlighting the impact today’s market is having on both homeowners… Read More